|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| assets | ||
| project | ||
| scripts/Murax | ||
| src | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| build.sbt | ||
README.md
Index
- Index
- Description
- Area usage and maximal frequency
- Dependencies
- CPU generation
- Regression tests
- Interactive debug of the simulated CPU via GDB OpenOCD and Verilator
- Using eclipse to run the software and debug it
- Briey SoC
- Murax SoC
- Build the RISC-V GCC
- CPU parametrization and instantiation example
- Add a custom instruction to the CPU via the plugin system
- Adding a new CSR via the plugin system
- CPU clock and resets
- VexRiscv Architecture
Description
This repository host an RISC-V implementation written in SpinalHDL. There is some specs :
- RV32I[M] instruction set
- Pipelined on 5 stages (Fetch, Decode, Execute, Memory, WriteBack)
- 1.44 DMIPS/Mhz when all features are enabled
- Optimized for FPGA, fully portable
- AXI4 and Avalon ready
- Optional MUL/DIV extension
- Optional instruction and data caches
- Optional MMU
- Optional debug extension allowing eclipse debugging via an GDB >> openOCD >> JTAG connection
- Optional interrupts and exception handling with the Machine and the User mode from the riscv-privileged-v1.9.1 spec.
- Two implementation of shift instructions, Single cycle / shiftNumber cycles
- Each stage could have bypass or interlock hazard logic
- FreeRTOS port https://github.com/Dolu1990/FreeRTOS-RISCV
- The data cache support atomic LR/SC
- RV32 compressed instruction are supported in the reworkFetch branch for configurations without instruction cache (will be merge in master, WIP)
The hardware description of this CPU is done by using an very software oriented approach (without any overhead in the generated hardware). There is a list of software concepts used :
- There is very few fixed things. Nearly everything is plugin based. The PC manager is a plugin, the register file is a plugin, the hazard controller is a plugin ...
- There is an automatic a tool which allow plugins to insert data in the pipeline at a given stage, and allow other plugins to read it in another stages through automatic pipelining.
- There is an service system which provide a very dynamic framework. As instance, a plugin could provide an exception service which could then be used by others plugins to emit exceptions from the pipeline.
There is a gitter channel for all questions about VexRiscv :
For commercial support, please contact spinalhdl@gmail.com
Area usage and maximal frequency
The following number where obtains by synthesis the CPU as toplevel without any specific synthesis option to save area or to get better maximal frequency (neutral).
The clock constraint is set to a unattainable value, which tends to increase the design area.
The dhrystone benchmark were compiled with -O3 -fno-inline
All the cached configuration have some cache trashing during the dhrystone benchmark except the VexRiscv full max perf one. This of course reduce the performance. It is possible to produce dhrystone binaries which fit inside a 4KB I$ and 4KB D$ (I already had this case once) but currently it isn't the case.
The used CPU corresponding configuration can be find in src/scala/vexriscv/demo.
VexRiscv smallest (RV32I, 0.52 DMIPS/Mhz, no datapath bypass, no interrupt) ->
Artix 7 -> 346 Mhz 481 LUT 539 FF
Cyclone V -> 201 Mhz 347 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 190 Mhz 673 LUT 529 FF
iCE40 -> 81 Mhz 1130 LC
VexRiscv smallest (RV32I, 0.52 DMIPS/Mhz, no datapath bypass) ->
Artix 7 -> 340 Mhz 562 LUT 589 FF
Cyclone V -> 202 Mhz 387 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 180 Mhz 780 LUT 579 FF
iCE40 -> 71 Mhz 1278 LC
VexRiscv small and productive (RV32I, 0.82 DMIPS/Mhz) ->
Artix 7 -> 327 Mhz 698 LUT 558 FF
Cyclone V -> 158 Mhz 524 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 146 Mhz 1,061 LUT 552 FF
iCE40 -> 55 Mhz 1541 LC
VexRiscv small and productive with I$ (RV32I, 0.72 DMIPS/Mhz, 4KB-I$) ->
Artix 7 -> 331 Mhz 727 LUT 600 FF
Cyclone V -> 152 Mhz 536 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 156 Mhz 1,075 LUT 565 FF
iCE40 -> 54 Mhz 1686 LC
VexRiscv full no cache (RV32IM, 1.22 DMIPS/Mhz, single cycle barrel shifter, debug module, catch exceptions, static branch) ->
Artix 7 -> 295 Mhz 1399 LUT 971 FF
Cyclone V -> 151 Mhz 922 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 136 Mhz 1,859 LUT 992 FF
VexRiscv full (RV32IM, 1.21 DMIPS/Mhz with cache trashing, 4KB-I$,4KB-D$, single cycle barrel shifter, debug module, catch exceptions, static branch) ->
Artix 7 -> 253 Mhz 1840 LUT 1394 FF
Cyclone V -> 126 Mhz 1,172 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 117 Mhz 2,548 LUT 1,703 FF
VexRiscv full max perf -> (RV32IM, 1.44 DMIPS/Mhz, 16KB-I$,16KB-D$, single cycle barrel shifter, debug module, catch exceptions, dynamic branch prediction in the fetch stage, branch and shift operations done in the Execute stage) ->
Artix 7 -> 183 Mhz 1813 LUT 1424 FF
Cyclone V -> 93 Mhz 1,253 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 84 Mhz 2,642 LUT 1,711 FF
VexRiscv full with MMU (RV32IM, 1.26 DMIPS/Mhz with cache trashing, 4KB-I$, 4KB-D$, single cycle barrel shifter, debug module, catch exceptions, dynamic branch, MMU) ->
Artix 7 -> 214 Mhz 2070 LUT 1913 FF
Cyclone V -> 108 Mhz 1,430 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 100 Mhz 2,976 LUT 2,201 FF
There is a summary of the configuration which produce 1.44 DMIPS :
- 5 stage : F -> D -> E -> M -> WB
- single cycle ADD/SUB/Bitwise/Shift ALU
- branch/jump done in the E stage
- memory load values are bypassed in the WB stage (late result)
- 33 cycle division with bypassing in the M stage (late result)
- single cycle multiplication with bypassing in the WB stage (late result)
- dynamic branch prediction done in the F stage with an direct mapped target buffer cache (no penalities on corrects predictions)
Dependencies
On Ubuntu 14 :
# JAVA JDK 7 or 8
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk
# SBT
echo "deb https://dl.bintray.com/sbt/debian /" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/sbt.list
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 2EE0EA64E40A89B84B2DF73499E82A75642AC823
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install sbt
# Verilator (for sim only, realy need 3.9+, in general apt-get will give you 3.8)
sudo apt-get install git make autoconf g++ flex bison
git clone http://git.veripool.org/git/verilator # Only first time
unsetenv VERILATOR_ROOT # For csh; ignore error if on bash
unset VERILATOR_ROOT # For bash
cd verilator
git pull # Make sure we're up-to-date
git tag # See what versions exist
autoconf # Create ./configure script
./configure
make
sudo make install
The VexRiscv need the unreleased master-head of SpinalHDL :
# Compile and localy publish the latest SpinalHDL
rm -rf SpinalHDL
git clone https://github.com/SpinalHDL/SpinalHDL.git
cd SpinalHDL
sbt clean compile publish-local
cd ..
CPU generation
You can find two example of CPU instantiation in :
- src/main/scala/vexriscv/GenFull.scala
- src/main/scala/vexriscv/GenSmallest.scala
To generate the corresponding RTL as a VexRiscv.v file, run (it could take time the first time you run it):
NOTE : The VexRiscv could need the unreleased master-head of SpinalHDL. If it fail to compile, just get the SpinalHDL repository and do a "sbt clean compile publish-local" in it as described in the dependencies chapter.
sbt "run-main vexriscv.demo.GenFull"
# or
sbt "run-main vexriscv.demo.GenSmallest"
Regression tests
To run tests (need the verilator simulator), go in the src/test/cpp/regression folder and run :
# To test the GenFull CPU
# (Don't worry about the CSR test not passing, basicaly the GenFull isn't the truly full version of the CPU, some CSR feature are disable in it)
make clean run
# To test the GenSmallest CPU
make clean run IBUS=SIMPLE DBUS=SIMPLE CSR=no MMU=no DEBUG_PLUGIN=no MUL=no DIV=no
Those self tested tests include :
- ISA tests from https://github.com/riscv/riscv-tests/tree/master/isa
- Dhrystone benchmark
- 24 tests FreeRTOS tests
- Some handwritten tests to check the CSR, debug module and MMU plugins
You can enable FreeRTOS tests by adding 'FREERTOS=yes' in the command line, will take time. Also, it use THREAD_COUNT host CPU threads to run multiple regression in parallel.
Interactive debug of the simulated CPU via GDB OpenOCD and Verilator
It's as described to run tests, but you just have to add DEBUG_PLUGIN_EXTERNAL=yes in the make arguments. Work for the GenFull, but not for the GenSmallest as this configuration has no debug module.
Then you can use the https://github.com/SpinalHDL/openocd_riscv tool to create a GDB server connected to the target (the simulated CPU)
#in the VexRiscv repository, to run the simulation on which one OpenOCD can connect itself =>
sbt "run-main vexriscv.demo.GenFull"
cd src/test/cpp/regression
make run DEBUG_PLUGIN_EXTERNAL=yes
#In the openocd git, after building it =>
src/openocd -c "set VEXRISCV_YAML PATH_TO_THE_GENERATED_CPU0_YAML_FILE" -f tcl/target/vexriscv_sim.cfg
#Run a GDB session with an elf RISCV executable (GenFull CPU)
YourRiscvToolsPath/bin/riscv32-unknown-elf-gdb VexRiscvRepo/src/test/resources/elf/uart.elf
target remote localhost:3333
monitor reset halt
load
continue
# Now it should print messages in the Verilator simulation of the CPU
Using eclipse to run the software and debug it
By using Zylin plugin
You can use the eclipse + Zylin embedded CDT plugin to do it (http://opensource.zylin.com/embeddedcdt.html). Tested with Helios Service Release 2 (http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/download.php?file=/technology/epp/downloads/release/helios/SR2/eclipse-cpp-helios-SR2-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz) and the corresponding zylin plugin.
To following commands will download eclipse and install the plugin.
wget http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/download.php?file=/technology/epp/downloads/release/helios/SR2/eclipse-cpp-helios-SR2-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -xvzf download.php?file=%2Ftechnology%2Fepp%2Fdownloads%2Frelease%2Fhelios%2FSR2%2Feclipse-cpp-helios-SR2-linux-gtk-x86_64.tar.gz
cd eclipse
./eclipse -application org.eclipse.equinox.p2.director -repository http://opensource.zylin.com/zylincdt -installIU com.zylin.cdt.feature.feature.group/
See https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1NseNHH05B6lmIXqQFVwK8xRjWE4ydeG-?usp=sharing to import a makefile project and create a debug configuration.
Note that sometime this eclipse need to be restarted in order to be able to place new breakpoints.
By using FreedomStudio
You can get FreedomStudio (which is package with eclipse and some plugins) there https://www.sifive.com/products/tools/
See https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1a7FyMOYgFc9UDhfsWUSCjyqDCvOrts2J?usp=sharing to import a makefile project and create a debug configuration.
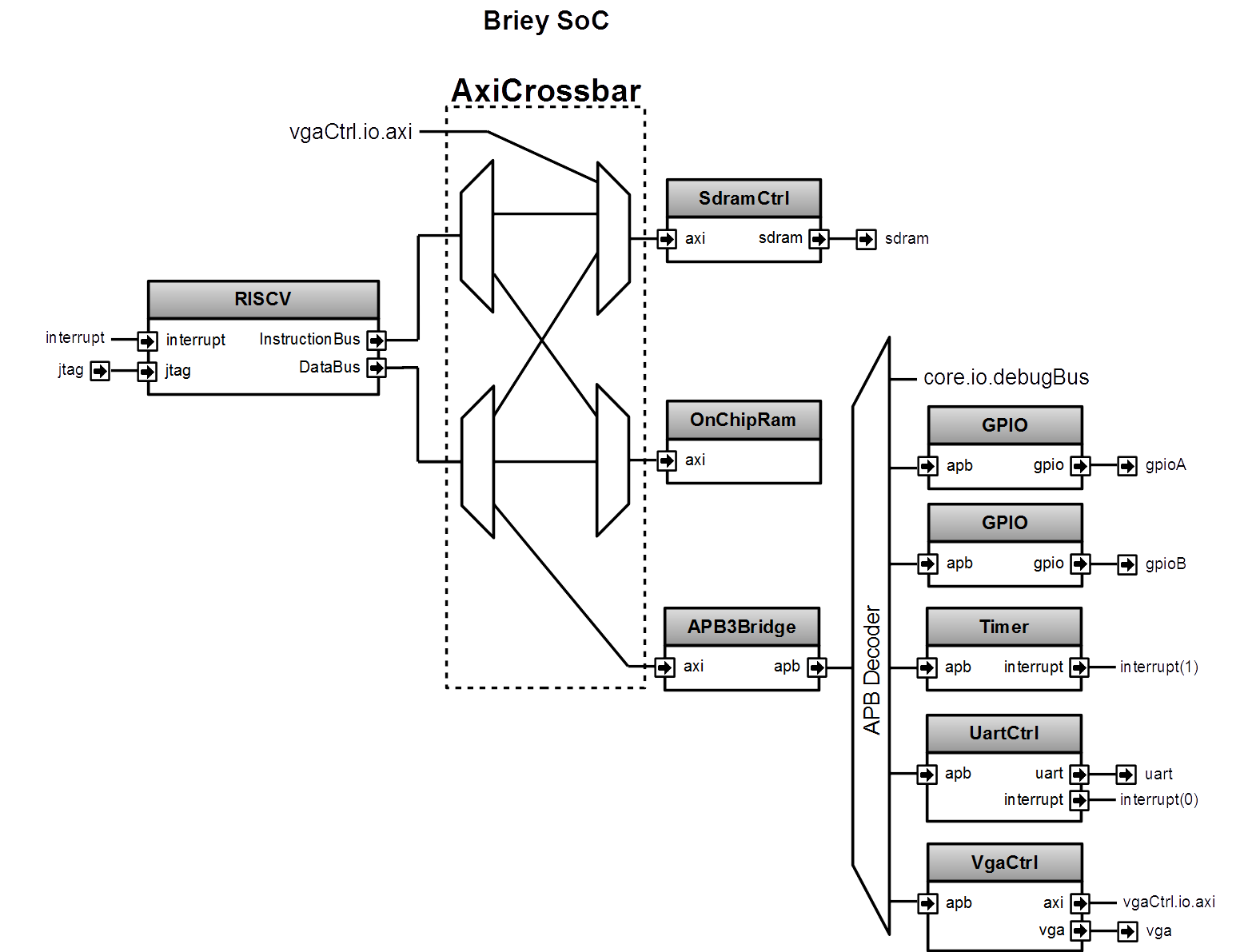
Briey SoC
As a demonstrator, a SoC named Briey is implemented in src/main/scala/vexriscv/demo/Briey.scala. This SoC is very similar to the Pinsec one :
To generate the Briey SoC Hardware :
sbt "run-main vexriscv.demo.Briey"
To run the verilator simulation of the Briey SoC which can be then connected to OpenOCD/GDB, first get those dependencies :
sudo apt-get install build-essential xorg-dev libudev-dev libts-dev libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev libasound2-dev libpulse-dev libopenal-dev libogg-dev libvorbis-dev libaudiofile-dev libpng12-dev libfreetype6-dev libusb-dev libdbus-1-dev zlib1g-dev libdirectfb-dev libsdl2-dev
Then go in src/test/cpp/briey and run the simulation with (UART TX is printed in the terminal, VGA is displayed in a GUI):
make clean run
To connect OpenOCD (https://github.com/SpinalHDL/openocd_riscv) to the simulation :
src/openocd -f tcl/interface/jtag_tcp.cfg -c "set BRIEY_CPU0_YAML /home/spinalvm/Spinal/VexRiscv/cpu0.yaml" -f tcl/target/briey.cfg
You can find multiples software examples and demo there : https://github.com/SpinalHDL/VexRiscvSocSoftware/tree/master/projects/briey
You can find some FPGA project which instantiate the Briey SoC there (DE1-SoC, DE0-Nano): https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B-CqLXDTaMbKZGdJZlZ5THAxRTQ?usp=sharing
There is some measurements of Briey SoC timings and area :
Artix 7 -> 239 Mhz 3227 LUT 3410 FF
Cyclone V -> 125 Mhz 2,207 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 112 Mhz 4,594 LUT 3,620
Murax SoC
Murax is a very light SoC (fit in ICE40 FPGA) which could work without any external component.
- VexRiscv RV32I[M]
- JTAG debugger (eclipse/GDB/openocd ready)
- 8 kB of on-chip ram
- Interrupt support
- APB bus for peripherals
- 32 GPIO pin
- one 16 bits prescaler, two 16 bits timers
- one UART with tx/rx fifo
Depending the CPU configuration, on the ICE40-hx8k FPGA with icestorm for synthesis, the full SoC will get following area/performance :
- RV32I interlocked stages => 51 Mhz, 2387 LC 0.45 DMIPS/Mhz
- RV32I bypassed stages => 45 Mhz, 2718 LC 0.65 DMIPS/Mhz
You can find its implementation there : src/main/scala/vexriscv/demo/Murax.scala
To generate the Murax SoC Hardware :
# To generate the SoC without any content in the ram
sbt "run-main vexriscv.demo.Murax"
# To generate the SoC with a demo program in the SoC
# Will blink led and echo UART RX to UART TX (in the verilator sim, type some text and press enter to send UART frames to the Murax RX pin)
sbt "run-main vexriscv.demo.MuraxWithRamInit"
Then go in src/test/cpp/murax and run the simulation with :
make clean run
To connect OpenOCD (https://github.com/SpinalHDL/openocd_riscv) to the simulation :
src/openocd -f tcl/interface/jtag_tcp.cfg -c "set MURAX_CPU0_YAML /home/spinalvm/Spinal/VexRiscv/cpu0.yaml" -f tcl/target/murax.cfg
You can find multiples software examples and demo there : https://github.com/SpinalHDL/VexRiscvSocSoftware/tree/master/projects/murax
There is some measurements of Murax SoC timings and area :
Murax interlocked stages (0.45 DMIPS/Mhz) ->
Artix 7 -> 305 Mhz 1004 LUT 1297 FF
Cyclone V -> 160 Mhz 744 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 148 Mhz 1,522 LUT 1,255 FF
ICE40-HX -> 51 Mhz 2402 LC (icestorm)
MuraxFast bypassed stages (0.65 DMIPS/Mhz) ->
Artix 7 -> 312 Mhz 1240 LUT 1330 FF
Cyclone V -> 159 Mhz 884 ALMs
Cyclone IV -> 142 Mhz 1,755 LUT 1,289 FF
ICE40-HX -> 50 Mhz, 2787 LC (icestorm)
There is some scripts to generate the SoC and call the icestorm toolchain there : scripts/Murax/
Note that now a toplevel simulation testbench with the same feature + a GUI is implemented with SpinalSim. You can find it in src/test/scala/vexriscv/MuraxSim.scala.
To run it :
#This will generate the Murax RTL + run its testbench. You need Verilator 3.9xx installated.
sbt "test:runMain vexriscv.MuraxSim"
Build the RISC-V GCC
In fact, now you can find some prebuild GCC :
- https://www.sifive.com/products/tools/ => SiFive GNU Embedded Toolchain The VexRiscvSocSoftware makefiles are expecting to find this prebuild version in /opt/riscv/contentOfThisPreBuild
wget https://static.dev.sifive.com/dev-tools/riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc-20171231-x86_64-linux-centos6.tar.gz
tar -xzvf riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc-20171231-x86_64-linux-centos6.tar.gz
sudo mv riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc-20171231-x86_64-linux-centos6 /opt/riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc-20171231-x86_64-linux-centos6
sudo mv /opt/riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc-20171231-x86_64-linux-centos6 /opt/riscv
echo 'export PATH=/opt/riscv/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc
But if you want to compile from sources in /opt/ the rv32i and rv32im gcc, do the following (will take one hour):
# Be carefull, sometime the git clone has issue to successfully clone riscv-gnu-toolchain.
sudo apt-get install autoconf automake autotools-dev curl libmpc-dev libmpfr-dev libgmp-dev gawk build-essential bison flex texinfo gperf libtool patchutils bc zlib1g-dev -y
git clone --recursive https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain riscv-gnu-toolchain
cd riscv-gnu-toolchain
echo "Starting RISC-V Toolchain build process"
ARCH=rv32im
rmdir -rf $ARCH
mkdir $ARCH; cd $ARCH
../configure --prefix=/opt/$ARCH --with-arch=$ARCH --with-abi=ilp32
sudo make -j4
cd ..
ARCH=rv32i
rmdir -rf $ARCH
mkdir $ARCH; cd $ARCH
../configure --prefix=/opt/$ARCH --with-arch=$ARCH --with-abi=ilp32
sudo make -j4
cd ..
echo -e "\\nRISC-V Toolchain installation completed!"
CPU parametrization and instantiation example
You can find many example of different config in the https://github.com/SpinalHDL/VexRiscv/tree/master/src/main/scala/vexriscv/demo folder. There is one :
import vexriscv._
import vexriscv.plugin._
//Instanciate one VexRiscv
val cpu = new VexRiscv(
//Provide a configuration instance
config = VexRiscvConfig(
//Provide a list of plugins which will futher add their logic into the CPU
plugins = List(
new PcManagerSimplePlugin(
resetVector = 0x00000000l,
relaxedPcCalculation = true
),
new IBusSimplePlugin(
interfaceKeepData = false,
catchAccessFault = false
),
new DBusSimplePlugin(
catchAddressMisaligned = false,
catchAccessFault = false
),
new DecoderSimplePlugin(
catchIllegalInstruction = false
),
new RegFilePlugin(
regFileReadyKind = Plugin.SYNC,
zeroBoot = true
),
new IntAluPlugin,
new SrcPlugin(
separatedAddSub = false,
executeInsertion = false
),
new LightShifterPlugin,
new HazardSimplePlugin(
bypassExecute = false,
bypassMemory = false,
bypassWriteBack = false,
bypassWriteBackBuffer = false
),
new BranchPlugin(
earlyBranch = false,
catchAddressMisaligned = false,
prediction = NONE
),
new YamlPlugin("cpu0.yaml")
)
)
)
Add a custom instruction to the CPU via the plugin system
There is an example of an simple plugin which add an simple SIMD_ADD instruction :
import spinal.core._
import vexriscv.plugin.Plugin
import vexriscv.{Stageable, DecoderService, VexRiscv}
//This plugin example will add a new instruction named SIMD_ADD which do the following :
//
//RD : Regfile Destination, RS : Regfile Source
//RD( 7 downto 0) = RS1( 7 downto 0) + RS2( 7 downto 0)
//RD(16 downto 8) = RS1(16 downto 8) + RS2(16 downto 8)
//RD(23 downto 16) = RS1(23 downto 16) + RS2(23 downto 16)
//RD(31 downto 24) = RS1(31 downto 24) + RS2(31 downto 24)
//
//Instruction encoding :
//0000011----------000-----0110011
// |RS2||RS1| |RD |
//
//Note : RS1, RS2, RD positions follow the RISC-V spec and are common for all instruction of the ISA
class SimdAddPlugin extends Plugin[VexRiscv]{
//Define the concept of IS_SIMD_ADD signals, which specify if the current instruction is destined for ths plugin
object IS_SIMD_ADD extends Stageable(Bool)
//Callback to setup the plugin and ask for different services
override def setup(pipeline: VexRiscv): Unit = {
import pipeline.config._
//Retrieve the DecoderService instance
val decoderService = pipeline.service(classOf[DecoderService])
//Specify the IS_SIMD_ADD default value when instruction are decoded
decoderService.addDefault(IS_SIMD_ADD, False)
//Specify the instruction decoding which should be applied when the instruction match the 'key' parttern
decoderService.add(
//Bit pattern of the new SIMD_ADD instruction
key = M"0000011----------000-----0110011",
//Decoding specification when the 'key' pattern is recognized in the instruction
List(
IS_SIMD_ADD -> True,
REGFILE_WRITE_VALID -> True, //Enable the register file write
BYPASSABLE_EXECUTE_STAGE -> True, //Notify the hazard management unit that the instruction result is already accessible in the EXECUTE stage (Bypass ready)
BYPASSABLE_MEMORY_STAGE -> True, //Same as above but for the memory stage
RS1_USE -> True, //Notify the hazard management unit that this instruction use the RS1 value
RS2_USE -> True //Same than above but for RS2.
)
)
}
override def build(pipeline: VexRiscv): Unit = {
import pipeline._
import pipeline.config._
//Add a new scope on the execute stage (used to give a name to signals)
execute plug new Area {
//Define some signals used internally to the plugin
val rs1 = execute.input(RS1).asUInt
//32 bits UInt value of the regfile[RS1]
val rs2 = execute.input(RS2).asUInt
val rd = UInt(32 bits)
//Do some computation
rd(7 downto 0) := rs1(7 downto 0) + rs2(7 downto 0)
rd(16 downto 8) := rs1(16 downto 8) + rs2(16 downto 8)
rd(23 downto 16) := rs1(23 downto 16) + rs2(23 downto 16)
rd(31 downto 24) := rs1(31 downto 24) + rs2(31 downto 24)
//When the instruction is a SIMD_ADD one, then write the result into the register file data path.
when(execute.input(IS_SIMD_ADD)) {
execute.output(REGFILE_WRITE_DATA) := rd.asBits
}
}
}
}
Then if you want to add this plugin to a given CPU, you just need to add it in its parameterized plugin list.
This example is a very simple one, but each plugin can really have access to the whole CPU
- Halt a given stage of the CPU
- Unschedule instructions
- Emit an exception
- Introduce new instruction decoding specification
- Ask to jump the PC somewhere
- Read signals published by other plugins
- override published signals values
- Provide an alternative implementation
- ...
As a demonstrator, this SimdAddPlugin was integrated in the src/main/scala/vexriscv/demo/GenCustomSimdAdd.scala CPU configuration and is self tested by the src/test/cpp/custom/simd_add application by running the following commands :
# Generate the CPU
sbt "run-main vexriscv.demo.GenCustomSimdAdd"
cd src/test/cpp/regression/
# Optionally add TRACE=yes if you want to get the VCD waveform from the simulation.
# Also you have to know that by default, the testbench introduce instruction/data bus stall.
# Note the CUSTOM_SIMD_ADD flag is set to yes.
make clean run IBUS=SIMPLE DBUS=SIMPLE CSR=no MMU=no DEBUG_PLUGIN=no MUL=no DIV=no DHRYSTONE=no REDO=2 CUSTOM_SIMD_ADD=yes
To retrieve the plugin related signals in the wave, just filter with simd.
Adding a new CSR via the plugin system
You can find two example about how to add custom CSR into the CPU via the plugin system there : https://github.com/SpinalHDL/VexRiscv/blob/master/src/main/scala/vexriscv/demo/CustomCsrDemoPlugin.scala
The first one (CustomCsrDemoPlugin) is adding an instruction counter and an clock cycle counter into the CSR mapping (and also do tricky stuff as a demonstration).
While the second one (CustomCsrDemoGpioPlugin) is creating an GPIO peripheral directly mapped into the CSR.
CPU clock and resets
Without the debug plugin, the CPU will have clk input and a reset input, which is very standard. But with the debug plugin the situation is the following :
- clk : As before, the clock which drive the whole CPU design, including the debug logic
- reset : Reset all the CPU states excepted the debug logics
- debugReset : Reset the debug logic of the CPU
- debug_resetOut : It is a CPU output signal which allow the JTAG to reset the CPU + the memory interconnect + the peripherals
So there is the reset interconnect in case you use the debug plugin :
VexRiscv
+------------------+
| |
toplevelReset >----+--------> debugReset |
| | |
| +-----< debug_resetOut |
| | | |
+--or>-+-> reset |
| | |
| +------------------+
|
+-> Interconnect / Peripherals
VexRiscv Architecture
VexRiscv is implemented via an 5 stages in order pipeline on which many optional and complementary plugins will add functionalities to provide a functional RISC-V CPU. This approach is completely unconventional and only possible on meta hardware description languages (SpinalHDL in the current case) but had proved its advantages via the VexRiscv implementation :
- You can swap/turn on/turn off parts of the CPU directly via the plugin system
- You can add new functionalities/instruction without having to modify any sources code of the CPU
- It allow the CPU configuration to cover a very large spectrum of implementation without cooking spagetti code
- To resume it allow your code base to truly produce a parametrized CPU design
So again, if you generate the CPU without any plugin, it will only contain the 5 stages definition and their basic arbitration, but nothing else, as everything else, including the program counter is added into the CPU via plugins.
Plugins
This chapter is describing plugins currently implemented.
- PcManagerSimplePlugin
- IBusSimplePlugin
- IBusCachedPlugin
- DecoderSimplePlugin
- RegFilePlugin
- HazardSimplePlugin
- SrcPlugin
- IntAluPlugin
- LightShifterPlugin
- FullBarrielShifterPlugin
- BranchPlugin
- DBusSimplePlugin
- DBusCachedPlugin
- MulPlugin
- DivPlugin
- MulDivIterativePlugin
- CsrPlugin
- StaticMemoryTranslatorPlugin
- MemoryTranslatorPlugin
- DebugPlugin
- YamlPlugin
PcManagerSimplePlugin
This plugin implement the programme counter and over an jump service to all plugins.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| resetVector | BigInt | Address of the program counter after the reset |
| relaxedPcCalculation | Boolean | By default jump have an asynchronous immediate effect on the program counter, which allow to reduce the branch penalties by one cycle but could reduce the FMax as it will combinatorialy drive the instruction bus address signal. To avoid this you can set this parameter to true, which will make the jump affecting the programm counter in a sequancial way, which will cut the combinatorial path but add one additional cycle of penalty when a jump occur. |
The jump interface implemented by this plugin allow all other plugin to request jumps. The stage argument specify from which stage the jump is asked, which will allow the PcManagerSimplePlugin plugin to manage priorities between jump requests.
trait JumpService{
def createJumpInterface(stage : Stage) : Flow[UInt]
}
This plugin operate into the prefetch stage.
IBusSimplePlugin
This plugin fetch instruction via a very simple and neutral memory interface going outside the CPU.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| interfaceKeepData | Boolean | Specify if the read response interface keep the data until the next one, or if it's only present a single cycle. |
| catchAccessFault | Boolean | If an the read response specify an read error and this parameter is true, it will generate an CPU exception trap |
There is the SimpleBus interface definition
case class IBusSimpleCmd() extends Bundle{
val pc = UInt(32 bits)
}
case class IBusSimpleRsp() extends Bundle with IMasterSlave{
val ready = Bool
val error = Bool
val inst = Bits(32 bits)
override def asMaster(): Unit = {
out(ready,error,inst)
}
}
case class IBusSimpleBus(interfaceKeepData : Boolean) extends Bundle with IMasterSlave{
var cmd = Stream(IBusSimpleCmd())
var rsp = IBusSimpleRsp()
override def asMaster(): Unit = {
master(cmd)
slave(rsp)
}
}
There is at least one cycle latency between que cmd and the rsp. the rsp.ready flag should be false after a cmd until the rsp is present.
Note that bridges are implemented to convert this interface into AXI4 and Avalon
This plugin fit in the fetch stage
IBusCachedPlugin
Simple and light multi way instruction cache.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| cacheSize | Int | Total storage capacity of the cache |
| bytePerLine | Int | Number of byte per cache line |
| wayCount | Int | Number of cache way |
| twoCycleRam | Boolean | Check the tags values in the decode stage instead of the fetch stage to relax timings |
| asyncTagMemory | Boolean | Read the cache tags in a asyncronus manner instead of syncronous one |
| addressWidth | Int | Address width, should be 32 |
| cpuDataWidth | Int | Cpu data width, should be 32 |
| memDataWidth | Int | Memory data width, could potentialy be something else than 32, but only 32 is currently tested |
| catchIllegalAccess | Boolean | Catch when an memory access is done on non valid memory address (MMU) |
| catchAccessFault | Boolean | Catch when the memeory bus is responding with an error |
| catchMemoryTranslationMiss | Boolean | Catch when the MMU miss a TLB |
Note : If you enable the twoCycleRam and and the wayCount is bigger than one, then the register file plugin should be configured to read the regFile in a asyncronus manner.
DecoderSimplePlugin
This plugin will provide instruction decoding capabilities to others plugins.
As instance, the pipeline hazard plugin will need to know, for a given instruction, if it is using the register file source 1/2 in order stall the pipeline until the hazard is gone. So to provide this kind of information, each plugin which implement an instruction will document to the DecoderSimplePlugin plugin this kind of informations.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| catchIllegalInstruction | Boolean | If set to true, instruction which have no decoding specification will generate an trap exception |
There is an usage example :
//Specify the instruction decoding which should be applied when the instruction match the 'key' pattern
decoderService.add(
//Bit pattern of the new instruction
key = M"0000011----------000-----0110011",
//Decoding specification when the 'key' pattern is recognized in the instruction
List(
IS_SIMD_ADD -> True,
REGFILE_WRITE_VALID -> True, //Enable the register file write
BYPASSABLE_EXECUTE_STAGE -> True, //Notify the hazard management unit that the instruction result is already accessible in the EXECUTE stage (Bypass ready)
BYPASSABLE_MEMORY_STAGE -> True, //Same as above but for the memory stage
RS1_USE -> True, //Notify the hazard management unit that this instruction use the RS1 value
RS2_USE -> True //Same than above but for RS2.
)
)
}
This plugin operate in the Decode stage
RegFilePlugin
This plugin implement the register file.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| regFileReadyKind | RegFileReadKind | Can bet set to ASYNC or SYNC. Specify the kind of memory read used to implement the register file. ASYNC mean zero cycle latency memory read, while SYNC mean one cycle latency memory read which can be mapped into standard FPGA memory blocks |
| zeroBoot | Boolean | Load all registers with zeroes at the beginning of simulations to keep everything deterministic in logs/traces |
This register file use an don't care read during write policy, so the bypassing/hazard plugin should take care of this.
HazardSimplePlugin
This plugin check the pipeline instruction dependencies and depending them, it will stop the instruction in the decoding stage or bypass the instruction results from the following stages to the decode stage.
As the register file is implemented with a don't care read during write policy, this plugin also have to manage hazard comming from this.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| bypassExecute | Boolean | Enable the bypassing of instruction results comming from the Execute stage |
| bypassMemory | Boolean | Enable the bypassing of instruction results comming from the Memory stage |
| bypassWriteBack | Boolean | Enable the bypassing of instruction results comming from the WriteBack stage |
| bypassWriteBackBuffer | Boolean | Enable the bypassing of the previous cycle register file written value |
SrcPlugin
This plugin muxes different inputs values to produce SRC1/SRC2/SRC_ADD/SRC_SUB/SRC_LESS values which are common values used by many plugins in the exectue stage (ALU / Branch / Load / Store).
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| separatedAddSub | RegFileReadKind | By default SRC_ADD/SRC_SUB are generated from a single controllable adder/substractor, but if this is set to true, it use separated adder/substractors |
| executeInsertion | Boolean | By default SRC1/SRC2 are generated in the Decode stage, but if this parameter is true, it is done in the Execute stage (It will relax the bypassing network) |
Excepted SRC1/SRC2, this plugin do everything at the begining of Execute stage.
IntAluPlugin
This plugin implement all ADD/SUB/SLT/SLTU/XOR/OR/AND/LUI/AUIPC instructions in the execute stage by using the SrcPlugin outputs. It is a realy simple plugin.
The result is injected into the pipeline directly at the end of the execute stage.
LightShifterPlugin
Implement SLL/SRL/SRA instructions by using an iterative shifter register, whill use one cycle per bit shift.
The result is injected into the pipeline directly at the end of the execute stage.
FullBarrielShifterPlugin
Implement SLL/SRL/SRA instructions by using an full barriel shifter, so it execute all shifts in a single cycle.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| earlyInjection | Boolean | By default the result of the shift is injected into the pipeline in the Memory stage to relax timings, but if this option is true it will be done in the Execute stage |
BranchPlugin
This plugin implement all branch/jump instructions (JAL/JALR/BEQ/BNE/BLT/BGE/BLTU/BGEU) with some optional branch prediction. Each of those branch prediction could have been implemented into separated plugins.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| earlyBranch | Boolean | By default the branch is done in the Memory stage to relax timings, but if this option is set it's done in the Execute stage |
| catchAddressMisaligned | Boolean | If a jump/branch is done in an unaligned PC address, it will fire an trap exception |
| prediction | BranchPrediction | Can be set to NONE/STATIC/DYNAMIC/DYNAMIC_TARGET to specify the branch predictor implementation, see bellow for more descriptions |
| historyRamSizeLog2 | Int | Specify the number of entries in the direct mapped prediction cache of DYNAMIC/DYNAMIC_TARGET implementation. 2 pow historyRamSizeLog2 entries |
Each miss predicted jumps will produce between 2 and 4 cycles penalty depending the earlyBranch and the PcManagerSimplePlugin.relaxedPcCalculation configurations
Prediction NONE
No prediction, each PC changes due to a jump/branch will produce a penalty.
Prediction STATIC
In the decode stage, if the instruction is an conditional branch pointing backward or an JAL, it branch it speculatively. If the speculation is right it the branch penality is reduced to a single cycle, else the standard penalty is applied.
Prediction DYNAMIC
It is the same than the STATIC prediction, excepted that to do the prediction, it use a direct mapped 2 bit history cache (BHT) which remember if the branch is more likely to be taken or not.
Prediction DYNAMIC_TARGET
This predictor is using a direct mapped branch target buffer (BTB) in the Fetch stage which store the PC of the instruction, the target PC of the instruction and a 2 bit history to remember if the branch is more likely to be taken or not. This is the most efficient branch predictor actualy implemented on VexRiscv as when the branch prediction is right, is produce no branch penalty. The down side is that this predictor has a long combinatorial path comming from the prediction cache read port to the programm counter by passing through the jump interface.
DBusSimplePlugin
This plugin implement the load and store instructions (LB/LH/LW/LBU/LHU/LWU/SB/SH/SW) via a simple and neutral memory bus going out of the CPU.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| catchAddressMisaligned | Boolean | If a memory access is done in an unaligned memory address, it will fire an trap exception |
| catchAccessFault | Boolean | If a memory read return an error, it will fire an trap exception |
| earlyInjection | Boolean | By default, the memory read values are injected into the pipeline in the WriteBack stage to relax the timings, if this parameter is true it's done in the Memory stage |
There is the DBusSimpleBus
case class DBusSimpleCmd() extends Bundle{
val wr = Bool
val address = UInt(32 bits)
val data = Bits(32 bit)
val size = UInt(2 bit)
}
case class DBusSimpleRsp() extends Bundle with IMasterSlave{
val ready = Bool
val error = Bool
val data = Bits(32 bit)
override def asMaster(): Unit = {
out(ready,error,data)
}
}
case class DBusSimpleBus() extends Bundle with IMasterSlave{
val cmd = Stream(DBusSimpleCmd())
val rsp = DBusSimpleRsp()
override def asMaster(): Unit = {
master(cmd)
slave(rsp)
}
}
Note that bridges are implemented to convert this interface into AXI4 and Avalon
There is at least one cycle latency between que cmd and the rsp. the rsp.ready flag should be false after a read cmd until the rsp is present.
DBusCachedPlugin
Single way cache implementation with a victime buffer, documentation WIP
MulPlugin
Implement the multiplication instruction from the RISC-V M extension. Its implementation was done in a FPGA friendly way by using 4 multiplication of 17*17 bits. The processing is fully pipelined between the Execute/Memory/Writeback stage. The results of the instructions is always inserted in the WriteBack stage.
DivPlugin
Implement the division/modulo instruction from the RISC-V M extension. It is done by a simple iterative manner which always take 34 cycles. The result is inserted into the Memory stage.
This plugin is now based on the MulDivIterativePlugin one.
MulDivIterativePlugin
This plugin implement the multiplication, division and modulo of the RISC-V M extension by an iterative manner, which is friendly for small FPGA which don't provide DSP blocks.
This plugin is able to unrool the iterative calculation process to reduce the number of cycles used to execute mul/div instructions.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| genMul | Boolean | Enable the multiplication support, can be set to false if you wan for instance to use the MulPlugin instead |
| genDiv | Boolean | Enable the division support |
| mulUnroolFactor | Int | Number of combinatorial stages used to speed up the multiplication, should be > 0 |
| divUnroolFactor | Int | Number of combinatorial stages used to speed up the division, should be > 0 |
The number of cycles used to execute a multiplication is '32/mulUnroolFactor' The number of cycles used to execute a division is '32/divUnroolFactor + 1'
Both mul/div are processed into the memory stage (late result)
CsrPlugin
Implement most of the Machine mode and a very little bit of the User mode specified in the RISC-V previlegied spec. The access mode of most of the CSR is parameterizable (NONE/READ_ONLY/WRITE_ONLY/READ_WRITE) to reduce the area usage of useless features.
(CsrAccess can be NONE/READ_ONLY/WRITE_ONLY/READ_WRITE)
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| catchIllegalAccess | Boolean | |
| mvendorid | BigInt | |
| marchid | BigInt | |
| mimpid | BigInt | |
| mhartid | BigInt | |
| misaExtensionsInit | Int | |
| misaAccess | CsrAccess | |
| mtvecAccess | CsrAccess | |
| mtvecInit | BigInt | |
| mepcAccess | CsrAccess | |
| mscratchGen | Boolean | |
| mcauseAccess | CsrAccess | |
| mbadaddrAccess | CsrAccess | |
| mcycleAccess | CsrAccess | |
| minstretAccess | CsrAccess | |
| ucycleAccess | CsrAccess | |
| wfiGen | Boolean | |
| ecallGen | Boolean |
If an interrupt occur, before jumping to mtvec, the plugin will stop the Prefetch stage and wait that all the instructions in the following stages end their execution.
If an exception occur, the plugin will kill the corresponding instruction, flush all previous instruction, and wait until the previously killed instruction reach the WriteBack stage before jumping to mtvec.
StaticMemoryTranslatorPlugin
Static memory translator plugin which allow to specify which range of the memory addresses is IO mapped and shouldn't be cached
MemoryTranslatorPlugin
Simple software refilled MMU implementation. Allow others plugins as DBusCachedPlugin/IBusCachedPlugin to instanciate memory address translation ports. Each port has a small dedicated fully associative TLB cache which is refilled from a larger software filled TLB cache via an query which will look up one entry per cycle.
DebugPlugin
This plugin implement enough CPU debug feature to allow a comfortable GDB/eclipse debugging. To access those debug feature it provide a simple memory bus interface, the JTAG interface is provided by another bridge, which allow to efficiently connect multiple CPU to the same JTAG.
| Parameters | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| debugClockDomain | ClockDomain | As the debug unit is able to reset the CPU itself, it should use another clock domain to avoid killing itself (only the reset wire should differ) |
The internals of the debug plugin are done in a manner which reduce the area usage and the FMax impact of this plugin.
There is the simple bus to access it, the rsp come one cycle after the request :
case class DebugExtensionCmd() extends Bundle{
val wr = Bool
val address = UInt(8 bit)
val data = Bits(32 bit)
}
case class DebugExtensionRsp() extends Bundle{
val data = Bits(32 bit)
}
case class DebugExtensionBus() extends Bundle with IMasterSlave{
val cmd = Stream(DebugExtensionCmd())
val rsp = DebugExtensionRsp()
override def asMaster(): Unit = {
master(cmd)
in(rsp)
}
}
There is the register mapping :
Read address 0x00 ->
bit 0 : resetIt
bit 1 : haltIt
bit 2 : isPipBusy
bit 3 : haltedByBreak
bit 4 : stepIt
Write address 0x00 ->
bit 4 : stepIt
bit 16 : set resetIt
bit 17 : set haltIt
bit 24 : clear resetIt
bit 25 : clear haltIt and haltedByBreak
Read Address 0x04 ->
bits (31 downto 0) : Last value written into the register file
Write Address 0x04 ->
bits (31 downto 0) : Instruction that should be pushed into the CPU pipeline for debug purposes
The OpenOCD port is there : https://github.com/SpinalHDL/openocd_riscv
YamlPlugin
This plugin offer a service to others plugin to generate an usefull Yaml file about the CPU configuration, it will contain, for instance, the sequence of instruction required to flush the data cache (information used by openocd)